What is the Renewable Fuel Standard?
The Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program was established in 2005 as part of the Energy Policy Act, which amended the Clean Air Act of 1963.(EPA) The RFS is a national policy that aims to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and expand the renewable fuels sector in the United States while reducing its reliance on imported oil. The policy requires a specified volume of renewable fuel to replace or reduce petroleum-based transportation fuel, heating oil or jet fuel. The RFS entails four renewable fuel categories: biomass-based diesel, cellulosic biofuel, advanced biofuel and total renewable fuel.
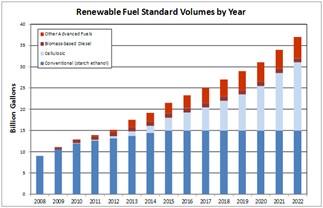
In 2007, the RFS was further amended by the Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA). EISA’s enactment significantly enhanced the RFS while establishing a long-term renewable fuel target of 36 billion gallons in 2022.
Renewable Natural Gas & The Renewable Fuel Standard
Renewable natural gas (RNG) or biomethane, is biogas that has been captured and upgraded so it can be used to substitute conventional natural gas. Biogas from sources such as landfills, livestock farms, wastewater treatment plants and food waste can be leveraged to produce RNG. Relative to the renewable fuel categories in the RFS, RNG is defined as cellulosic biofuel.(EPA)
When RNG is used as a transportation fuel, Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs) are generated. RINs are credits that can be utilized by obligated parties, refiners and importers of gasoline or diesel fuel, to demonstrate compliance with the Renewable Volume Obligation (RVO) that is set within the RFS.
The RFS has been essential to accelerating the adoption of RNG and other renewable fuels, reducing emissions and enabling the expansion of the RNG industry. According to the Natural Gas Vehicles for America (NGVAmerica) and Coalition of Renewable Natural Gas (RNG Coalition), RNG accounted for 69% of on-road natural gas vehicle fuel in 2022.(NGVAmerica & RNG Coalition)
Updating the Renewable Fuel Standard
With the RVO previously set through 2022, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has undergone the process of updating the RFS. Below is a timeline of events leading up to the RFS update released on June 21, 2023.
December 2022: The EPA announced a proposed rule to establish the volume and percentage standards for 2023, 2024 and 2025.(EPA) The original proposal also entailed modifications to strengthen and expand the RFS. One of the modifications aimed to spur electric vehicle adoption by establishing a pathway for electric vehicle manufacturers to generate electric RINs (eRINs).(Reuters) eRINs would be produced when qualifying biogas is used to generate renewable electricity for the charging of light-duty electric vehicles. Similar to RINs, obligated parties could leverage eRINs to exhibit RVO compliance.
January 2023: Throughout January and February 2023, the EPA held a public hearing and received comments from industry stakeholders on the originally proposed rule.
May 2023: On May 1, it was reported that the eRIN program may be delayed.(Reuters) The originally proposed rule from December 2022 planned for the eRIN program to be implemented on January 1, 2024. On May 5, stakeholders spanning the RNG Coalition, American Biogas Council, Alliance for Automotive Innovation, Business Council for Sustainable Energy, Zero Emission Transportation Association, National Milk Producers Federation and National Association of Clean Water Agencies urged the EPA to move forward with the eRIN proposal.(RNG Coalition) On May 15, the EPA submitted a draft of the final RFS rule to the White House Office of Management and Budget.(SPC Global) On May 23, the EPA recommended delaying the eRINs program.(Reuters)
June 2023: Originally scheduled to be released on June 14, 2023, the EPA filed and was granted an extension to release the final RFS rule on June 21, 2023.(U.S. News & World Report)
The EPA finalized and released the 2023 RFS update on June 21, 2023. The updated ruling increased renewable volume obligations for cellulosic biofuel to 0.84 billion gallons in 2023, 1.09 billion gallons in 2024 and 1.38 billion gallons in 2025. The increased obligations are expected to continue driving RNG production forward and enabling greater development of the turnkey renewable energy. Consistent with the indication in May 2023, the eRIN program has been delayed.
| Volume Targets (billion RINs)a(EPA) | |||
| 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | |
| Cellulosic biofuel | 0.84 | 1.09 | 1.38 |
| Biomass-based dieselb | 2.82 | 3.04 | 3.35 |
| Advanced biofuel | 5.94 | 6.54 | 7.33 |
| Renewable Fuel | 20.94 | 21.54 | 22.33 |
| Supplemental standard | 0.25 | n/a | n/a |
a - One RIN is equivalent to one ethanol-equivalent gallon of renewable fuel.
b - BBD is given in billion gallons
b - BBD is given in billion gallons
Moving the RNG Industry Forward
In response to the updated RFS, Aaron Johnson, President of Renewable Natural Gas said, “We commend the EPA for taking a fresh look at the data and appropriately increasing the RVO’s. We also encourage them to address the significant concerns regarding the original eRIN proposal raised by multiple stakeholders.”
Kinetrex Energy, a Kinder Morgan company, is a leading RNG solutions provider that simplifies the development and adoption of RNG. Our RNG development capabilities enable landfills to convert their landfill gas to renewable energy, reducing emissions and maximizing value. For organizations looking to reduce their environmental impact, we provide a turnkey RNG solution that can be seamlessly implemented with your existing operations.

